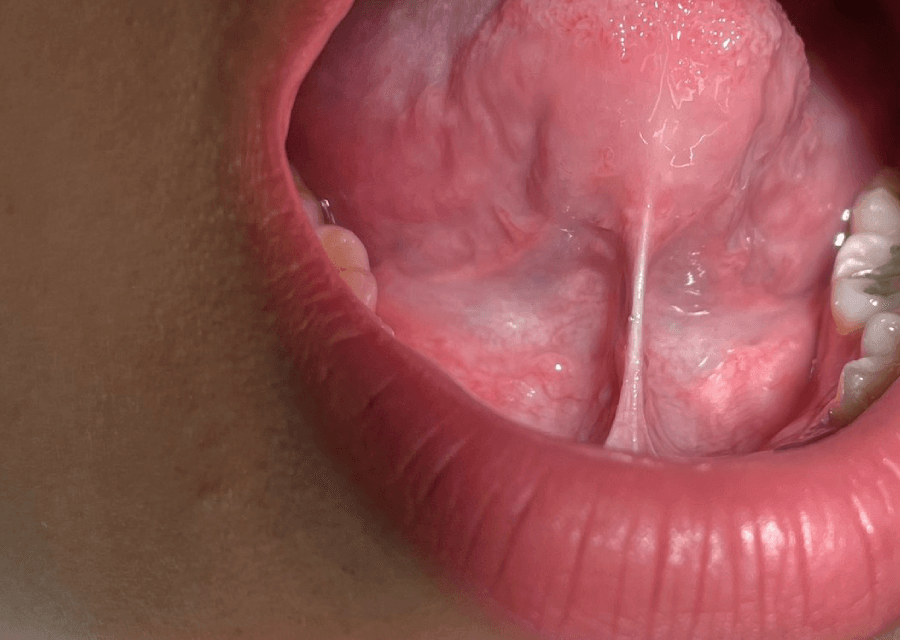
Tongue tie, also known as ankyloglossia, is a condition where the thin piece of tissue (called the frenulum) under the tongue is too short or tight, restricting the tongue’s movement. This condition can cause difficulties in breastfeeding, speaking, eating and even maintaining proper oral hygiene. If your child (or even you) is diagnosed with tongue tie, it’s important to understand how the condition is diagnosed and the available treatment options.
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the process of managing tongue tie—from diagnosis to treatment—so you can make informed decisions about the best course of action for yourself or your child.
Step 1: Recognizing the Symptoms of Tongue Tie
Tongue tie can vary in severity and its symptoms can be different for each person. Here are some common signs and symptoms to look for:
For Babies:
- Breastfeeding difficulties: Babies with tongue tie may have trouble latching properly or may have trouble sucking effectively, which can lead to poor weight gain.
- Pain for the mother: If the baby is unable to latch properly, the mother may experience nipple pain or damage during breastfeeding.
- Clicking sound: Some babies make a clicking sound while feeding because they struggle to maintain suction.
- Inadequate milk transfer: Even with extended feeding sessions, the baby may not seem satisfied or may be fussy after feedings.
For Children and Adults:
- Speech difficulties: Tongue tie can cause problems with pronouncing certain sounds, such as “t,” “d,” “l,” and “s.”
- Difficulty with eating: Older children or adults with tongue tie may have trouble eating certain foods, especially those that require the tongue to move freely, like chewing or swallowing.
- Oral hygiene issues: The restricted tongue movement can make it difficult to clean the mouth properly, increasing the risk of tooth decay or gum disease.
- Pain or discomfort: Sometimes, the tight frenulum can cause pain or discomfort when speaking, swallowing or even sticking out the tongue.
If you or your baby are experiencing any of these symptoms, it may be time to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a pediatrician, dentist or speech therapist, to determine whether tongue tie is the cause.
Step 2: Diagnosis of Tongue Tie
Diagnosing tongue tie is usually a simple process that involves a physical examination of the mouth. A healthcare professional will look at the structure of the frenulum and assess how it affects the movement of the tongue.
For babies, a pediatrician or lactation consultant will often diagnose tongue tie if there are feeding issues. For older children and adults, the diagnosis may come from a dentist, speech therapist or even an orthodontist, especially if there are speech or eating problems.
There are different types of tongue tie, classified by the severity of the restriction:
- Mild: The frenulum may be slightly tight, but the tongue can still move freely.
- Moderate: The frenulum is tighter and there is some limitation in tongue movement.
- Severe: The frenulum is very tight and the tongue is restricted in its range of motion, affecting speech, eating and oral hygiene.
In some cases, further assessments may be done, including speech evaluations or a consultation with a lactation consultant, especially if breastfeeding is a concern.
Step 3: Treatment Options for Tongue Tie
If a diagnosis of tongue tie is confirmed, treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms. In some cases, no treatment is necessary, but if the tongue tie is causing significant issues, there are several treatment options available.
- Observation and Monitoring
In mild cases, a healthcare provider may suggest simply monitoring the condition over time. Sometimes, babies grow out of tongue tie as they develop better muscle control and the issue may resolve itself without intervention. If there are no significant feeding or speech problems, your doctor may advise waiting and continuing to monitor the situation.
- Stretching Exercises
For some children and adults, stretching exercises can help improve the movement of the tongue and reduce the tightness of the frenulum. These exercises are usually performed under the guidance of a speech therapist or pediatric dentist. While stretching is a non-invasive treatment, it may not be effective for more severe cases of tongue tie.
- Frenotomy (Frenulectomy)
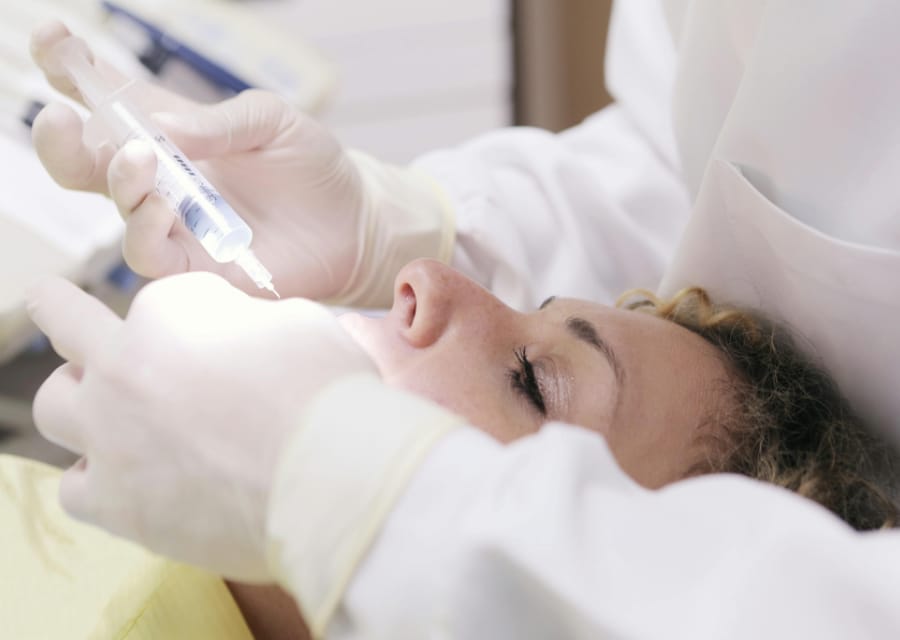
For more severe cases, frenotomy or frenulectomy is a common treatment option. This procedure involves the simple release of the tight frenulum by making a small cut or incision. It can usually be done quickly and with minimal pain. Frenotomy is often performed in infants with feeding difficulties and can be done in a pediatrician’s office or a dentist’s office with local anesthesia.
For infants, a frenotomy is typically a quick procedure that takes only a few minutes and may not require stitches. After the procedure, the baby can usually breastfeed immediately. The recovery process is often short and the baby may experience some discomfort, but complications are rare.
- Frenuloplasty
Frenuloplasty is a more extensive procedure used for severe cases of tongue tie or when a frenotomy alone is not sufficient. It involves a more precise surgical procedure to release the frenulum and reshape it to allow for improved tongue movement. Frenuloplasty may require local anesthesia or even general anesthesia, depending on the age and severity of the condition.
This procedure is more commonly performed in older children and adults who may have more significant speech or eating problems due to tongue tie. After the procedure, physical therapy and stretching exercises are often recommended to help ensure the tongue moves properly.
- Speech Therapy
In some cases, speech therapy may be recommended after a frenotomy or frenuloplasty, especially for children or adults who have difficulty with speech due to tongue tie. A speech therapist will guide the patient through exercises to improve tongue mobility and enhance speech clarity.
Step 4: Aftercare and Recovery
After treatment, especially if a frenotomy or frenuloplasty was performed, some aftercare will be required to ensure proper healing and maximize the benefits of the procedure. Here’s what you can expect:
For Babies:
- Breastfeeding: After a frenotomy, babies are usually able to breastfeed right away. In some cases, they may need a few days to adjust to the new tongue movement.
- Mouth exercises: Parents may be advised to perform simple stretching exercises or massaging the baby’s tongue to help prevent the frenulum from reattaching in a restricted position.
For Older Children and Adults:
- Follow-up appointments: A follow-up visit will be scheduled to check on healing and ensure the tongue is moving freely.
- Stretching exercises: Ongoing stretching exercises may be recommended to ensure the tongue’s full range of motion.
- Speech therapy: If speech was affected, working with a speech therapist may be necessary to correct speech patterns.
Step 5: Preventing Future Problems
After treatment, it’s important to continue monitoring for any potential issues. In some cases, even after treatment, the frenulum may reattach or cause additional problems. Regular dental and speech check-ups can help ensure that your tongue’s movement remains free and that there are no ongoing difficulties with eating, speaking or oral hygiene.
Conclusion
Managing tongue tie is an important process that requires careful attention and timely intervention. From recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis to deciding on the best treatment options, understanding tongue tie is crucial for ensuring a healthy and comfortable life. Whether you’re dealing with breastfeeding issues for a newborn or speech difficulties as an adult, there are effective treatments available that can improve the quality of life.
If you suspect that you or your child may have tongue tie, the first step is to consult with a healthcare provider or dental professional. They can help guide you through the diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment based on your specific needs. With the right approach, managing tongue tie can lead to significant improvements in daily activities and overall well-being.
To schedule an appointment at ‘Sukumar Dental Clinic’ call +91-7418210108 or WhatsApp Dr. Sukumar at +91-9655225002. We take pride in having the top dental clinic in Palayamkottai, Tirunelveli. Alternatively, you can email us at info@sukumardental.com